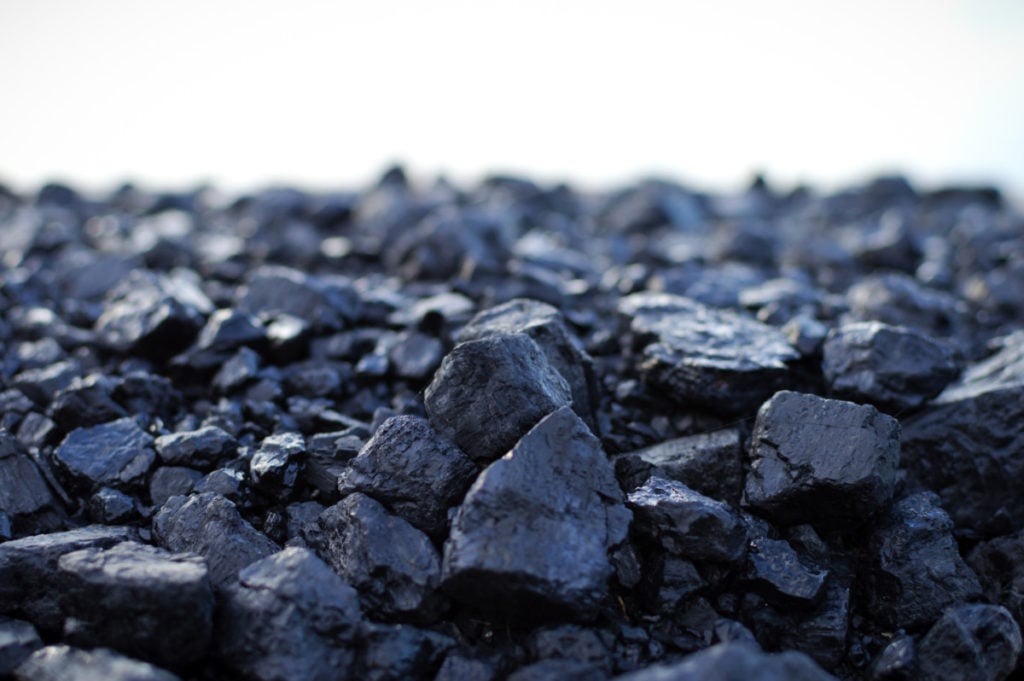
Coal is a sedimentary rock that is formed from decaying fragments of plants (early gymnosperms, club mosses, horsetails, tree-like ferns).
The rock being developed now was formed a very long time ago, 300-350 million years ago. The composition of coal includes high-molecular chemical compounds (mainly carbon), volatile substances with a small part of impurities and water. The value of coal depends on the amount of energy released during combustion and the resulting ash.
Coal properties
The properties of coal are determined by many factors, in particular, the place of extraction and the organization of storage. Therefore, it will be correct to give only averaged parameters:
- Volatile content: 39 to 41%;
- % ash: 14-16%;
- Percentage of sulfur: 0.5%;
- calorie content: from 5400 to 7000 kcal/kg;
- Moisture value: 13-15%.
Benefits of hard coal

Benefits of using coal as a fuel:
- high degree of heat transfer;
- relatively low cost (depending on the type of coal);
- complete combustion.
Coal classification
There are several ways to classify hard coal, for example, according to the degree of coalification and size class. So, according to the degree of coalification, hard coal is divided into:
- brown;
- stone;
- anthracite
Depending on the size class, coal is:
- slab;
- large;
- walnut;
- small;
- seed;
- stuff;
- Private.
Use of hard coal
Coal is mainly used as an energy and household fuel and as a raw material for the metallurgical industry and the production of macromolecular compounds. In the same way, coal is the raw material for rare trace elements used in the manufacture of medicines, perfumes, plastics, varnishes, paints, and much more.