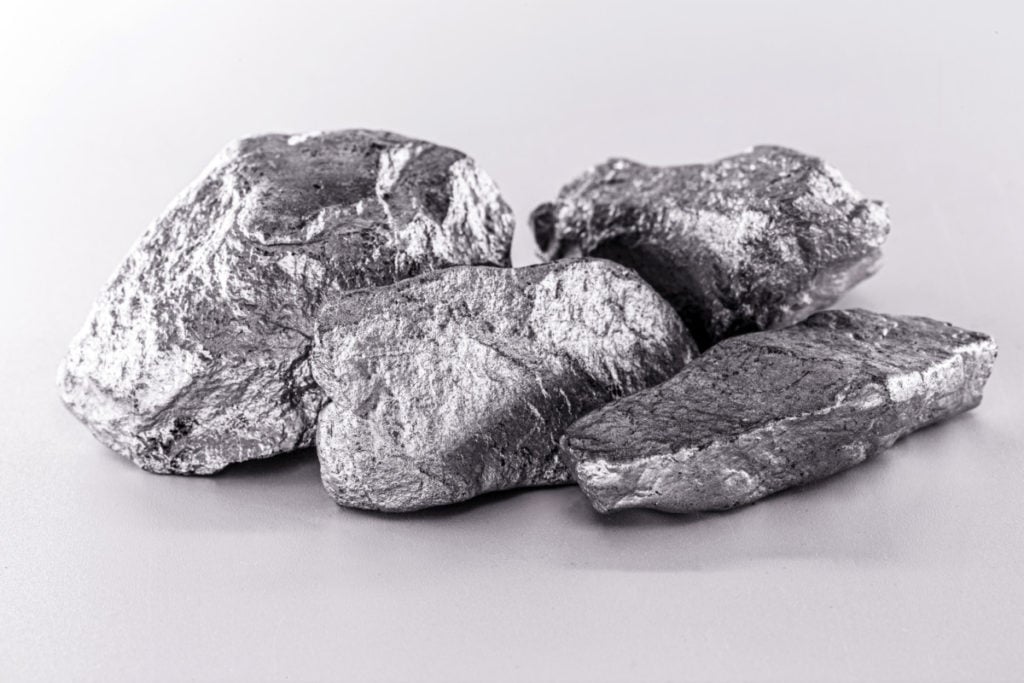
Platinum is a chemical element, a metal (the formula of platinum is Pt), and, moreover, very rare.
However, this does not negate a wide range of its application – from jewelry to pacemakers.
The history of the discovery and the origin of the name of the metal
The first mention of this substance dates back to 1557, when the Italian physician and humanist Julius Caesar Scaliger described the metal he found in Central America. It was not possible to melt this metal with the means and methods that existed at that time and were available to the Spanish conquistadors. Therefore, Scaliger called the new chemical substance platinum, which can be translated as “little silver” or even “silver”.
This name reflected both the color of the metal (silver-white) and its practical uselessness to the people of that era. Therefore, in the beginning, ancient metallurgists in Egypt and America used the metal to make jewelry and decorative items, mixing it with more fusible gold.
Perhaps that is why the metal was called white gold for a long time. The analogies were obvious – it, like gold, proved to be extremely resistant to tarnishing and corrosion. On the other hand, the element is very plastic and malleable: it can be easily deformed, drawn into a wire, etc. Finally, platinum is a full-fledged noble metal, since it does not oxidize and is not exposed to common acids.
Being in nature. Isotopes
World reserves of platinum are small. The metal content in the earth’s crust is 5 · 10-7 wt.%. It is found both in pure form and in compounds. The most important minerals are polyxene, which contains 6–10% iron, as well as palladium platinum, ferroplatinum, iridoplatinum, PtAs2 sperrylite, and a number of more complex chemical compounds, including nickel, sulfur, and palladium.
The best known of these minerals is braggite. It occurs together with copper and iron pyrites in contact with gold ore, crystallizing in cubic or, more rarely, octahedral form. Braggite has a metallic luster and also contains traces of rhodium and antimony.

To date, scientists have discovered quite a few isotopes of this element: 6 natural and 37 artificial. The most common isotopes:
- Pt195 (33.83% of the total).
- Pt194 (32.97% of the total).
- Pt196 (25.24% of the total).
- Pt198 (7.16% of the total).
- Pt192 (0.78% of total).
- Pt190 (0.01% of total).
Deposits
Platinum mining in the world is concentrated in South Africa (80% of the world’s production), Russia and Canada. Latin American platinum only reached Europe in 1735. The metal has also been found in Brazil in the mineral syenite, where it is found along with gold.
Where is platinum mined? Among the largest deposits:
- Ural alluvial deposits found in the Nizhny Tagil region;
- Lapland mines (Finland), where the metal is bound together with diamonds;
- Deposits in the Canadian provinces of Ontario and British Columbia, as well as in the vast areas adjacent to the Yukon Valley.
Deposits of platinum in Russia, in addition to the Urals, are also located beyond the Arctic Circle, in the region of Norilsk. Germany (the Rhine Valley), Indonesia (the island of Borneo), Spain, Ireland, the USA, Australia and New Zealand are also formally considered countries for the extraction of platinum. The volume of production there is small and does not yet have world economic significance.
Of the exotic methods of obtaining, it is worth mentioning meteoric iron, which often contains this metal.
Mining and production technologies
How is platinum mined? The method of extraction is determined by the form of finding platinum in nature, in the feedstock. For example, most of the platinum ore mined in British Columbia is rough and in the form of nuggets found in relatively small areas. Nuggets in their weight rarely exceed half an ounce (14 grams). Most of the metal occurs in small grains, which are separated by platinum producers into magnetic and non-magnetic. The latter make up a large proportion of the total.

Pure metal often contains traces of nickel, as evidenced by spectrochemical studies of samples from Russia, Spain and America. For example, when platinum is mined in Russia, samples from Kitlim contain at least 0.1% nickel, and Nizhny Tagil magnetic raw materials contain up to 0.75% nickel.
Physical properties
The element is one of the densest – 21,450 kg / m3, which is more than 21 times the density of water or 6 times the density of diamond. Among the main properties of this metal:
- The atomic weight is 195.1.
- Melting point -1768.4 0С.
- Boiling point – 3825 0C.
For industrial applications, the magnetic properties of a given metal matter. The non-magnetic form is more common, it has an increased density. Magnetic properties are determined by the presence of iron in the ore. Interestingly, some samples of the Ural platinum attract iron filings more strongly than an ordinary magnet.
Chemical properties
The first chemical studies were carried out as early as 1741 by the British scientist Charles Wood. It was he who first called this element a metal (the eighth among those known at that time), and described some of the characteristics of platinum.
Reactivity
The history of platinum includes testing for “nobility”. The metal passed it thanks to the research of British chemists William Wollaston and Smithson Tennant. At the beginning of the 19th century, they tried to dissolve purified platinum in a mixture of nitric and hydrochloric acids. After the metal was separated from the rest of the solution, palladium, rhodium, osmium, iridium, and later ruthenium were found in the waste.
It is characteristic that today mining is carried out according to a similar technology: samples containing the element are dissolved in an acidic environment, separated from the rest of the solution and by-products, and melted at very high temperatures to obtain pure metal.
Application of platinum
Platinum cylinders have long been used as the international standard for measuring weight. Now the metal is used to create high-strength parts for various machines, tools and jewelry. Due to its very low level of reactivity, the element is used in some anti-cancer drugs.

According to the latest data, about half of cancer patients use platinum-containing drugs, since the antitumor properties of platinum are already well understood. The metal is also used in pacemakers, dental crowns, and other devices due to its high resistance to corrosion from body fluids and lack of reactivity to vital functions.
Where else is platinum used? In combination with cobalt, this metal is used to create strong permanent magnets that are used in clockwork, motors, and medical equipment. Approximately one third of the world’s consumption of platinum as a precious metal falls on jewelry. In particular, most large diamonds are inserted into platinum cases.
Catalysts
Almost half of the platinum mined is used in catalytic converters – vehicle components that reduce exhaust emissions to acceptable levels.
They can withstand the high temperatures required for oxidation reactions, during which the toxicity of emissions is reduced. In addition, platinum is used as a catalyst in the production of fertilizers, plastics and gasoline.
Monetary functions. Insignia
Since platinum is a precious metal, in many countries it is stored in the form of bars that can be used for interbank payments. Commemorative signs are also produced. However, due to limited reserves, the volume of production of such items, in comparison with gold or silver, is small.
Platinum price and forecast
Annual production does not exceed 120…130 tons. Investment activity in the market is determined by significant price fluctuations. How much is platinum worth? Starting from February 2018, the cost of platinum has been falling, and, according to experts, it is projected at the level of 29…32 US dollars per gram.
However, the exchange rate of platinum and the dynamics of prices in recent years are seasonal: by the summer, the price of the metal usually increases. The forecast for platinum for 2018 indicates that the investment risks from investing are quite high: over the past 6 years, the price of a gram of this metal has almost halved: from 59 to 31 US dollars per gram.
Interesting facts about platinum
- The largest platinum nugget ever found weighed 7837 g.
- Wood based his research on documents confiscated by the British Navy from the Spanish scientist and naval officer Antonio de Ulloa, which date back to 1735.
- The element was first discovered in the alluvial deposits of the Pinto River, which flows through the territory of Colombia.