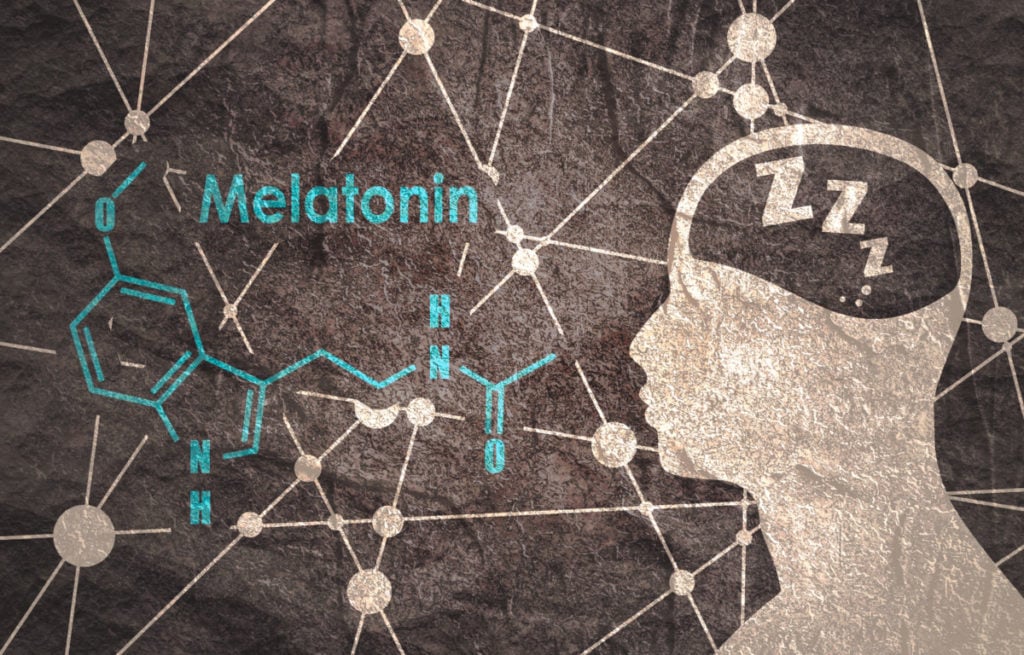
Sleep is a very specific state of the body in which the biochemistry changes significantly compared to the sunny and active part of the day. The most characteristic of these changes is an increase in the level of melatonin, commonly known as the sleep hormone.
When melatonin is produced
The adventure of melatonin in the body begins each day after dark when it leaves the pineal gland and enters the circulation.
Its production depends on the level of illumination received by the retina. Therefore, if you sit in bright light or look at the screen of a computer or phone until the last minute before bed, this reduces its production.

The biological effects of melatonin are caused by the activation of specific melatonin receptors, designated as MT1 and MT2. There was also a third MT3 “receptor”, but in his case it was later found to be only the quinone reductase II enzyme, so the receptor titer was no longer active. The MT1 and MT2 receptors are very different from each other in terms of induced effects.
MT1:
- suppresses the activity of neurons of the suprachiasmatic nuclei
- suppresses the release of GHRH into the hypothalamus
- suppresses the secretion of cortisol in the adrenal glands
- suppress testosterone in the testicles
- suppresses LH, FSH and prolactin in the pituitary
- suppresses the growth of fat cells
- causes vasoconstriction
MT2:
- suppresses the release of GHRH into the hypothalamus
- suppresses retinal dopamine release
- causes vasodilation
The above effects relate in particular to activation by endogenous melatonin at physiological concentrations. However, this may change slightly when more melatonin is administered externally, and also depending on concomitant factors such as the sex and age of the individual or the time of day.
Effect of melatonin on the human body
Regulation of oxidative stress
This hormone is also a fairly powerful antioxidant.
Controlling oxidative stress is one of the main aspects of health that you need to take care of in order to live a long and happy life. By reducing free radicals, melatonin has a neuroprotective effect and may reduce the risk of cancer.
Influence on sex hormones
Melatonin inhibits the activation of aromatase (an enzyme that converts androgens to estrogens) caused by cortisol. This occurs at melatonin concentrations corresponding to physiological.

On the other hand, in postmenopausal women who have previously won the fight against breast cancer, a 4-month intake of 3 mg of melatonin does not affect the level of estradiol. In this area, the action of melatonin is rather subtle, and it can be used as a supplement, but not as the main therapeutic agent in case of an estradiol / testosterone ratio disorder.
Growth hormone stimulation
Melatonin can influence the regulation of growth hormone (GH) and other hormones with which it has various relationships: GHRH, prolactin, somatostatin.
Opinions vary widely – some are staunch supporters of melatonin, believing that it greatly increases GH and all the benefits that come with it, while others are coldly skeptical about the realization that the increase in prolactin is unacceptable.
Body Enhancement
So how does melatonin affect your body shape? For example, it converts white body fat to brown (so-called darkened fat) and improves insulin sensitivity. Studies have shown that melatonin supplementation can help reduce visceral (abdominal) fat and even slightly reshape your figure.
The latter was noted with long-term use, but did not depend on diet and physical activity. Long term in this case refers to a year of taking 1–3 mg of melatonin at bedtime. The study involved postmenopausal women, and the results showed a greater reduction in fat mass and an increase in muscle mass than in the placebo group.
Influence on the digestive system
There is good news for people suffering from acid reflux. Taking melatonin for several weeks reduces the symptoms of acid reflux. Although the combination is not as effective as omeprazole, it gives better results than omeprazole alone.