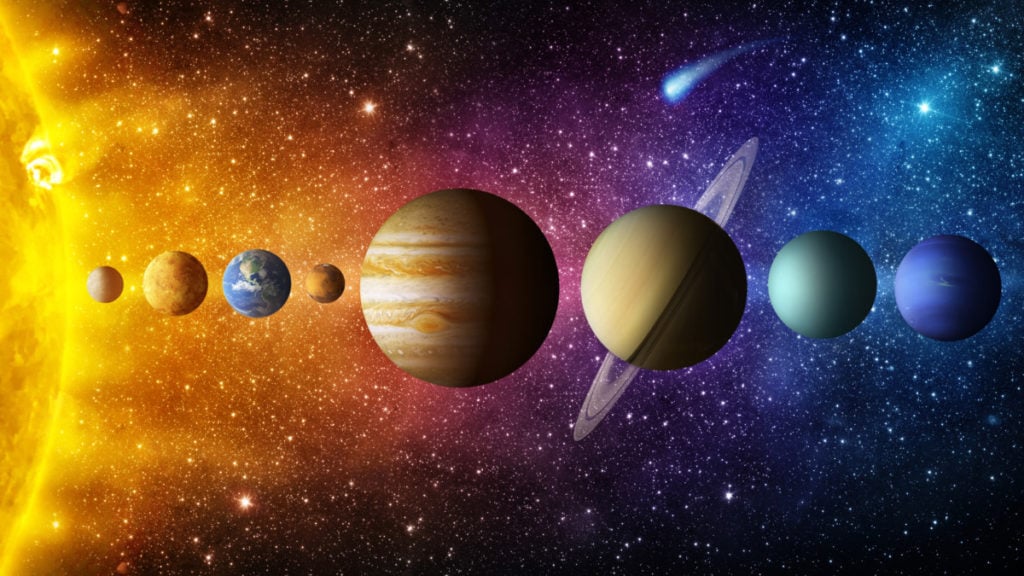
The Solar System is a planetary system in the Milky Way galaxy in which the Sun is the central star. Billions of celestial bodies are gravitationally bound to the Sun.
Among the celestial bodies are eight planets with several hundred moons revolving around them, as well as dwarf planets, asteroids, comets and many other smaller objects.
How many planets are in the solar system?
In addition, there are five dwarf planets in the planetary system: Ceres, Pluto (until recently considered the ninth full-fledged planet), Haumea, Makemake, and Eris. Six of the eight major planets and four of the five dwarf planets have natural satellites. Almost all planets are named after gods known from Roman mythology. Uranus owes its name to the Greek god of the sky.
Mercury
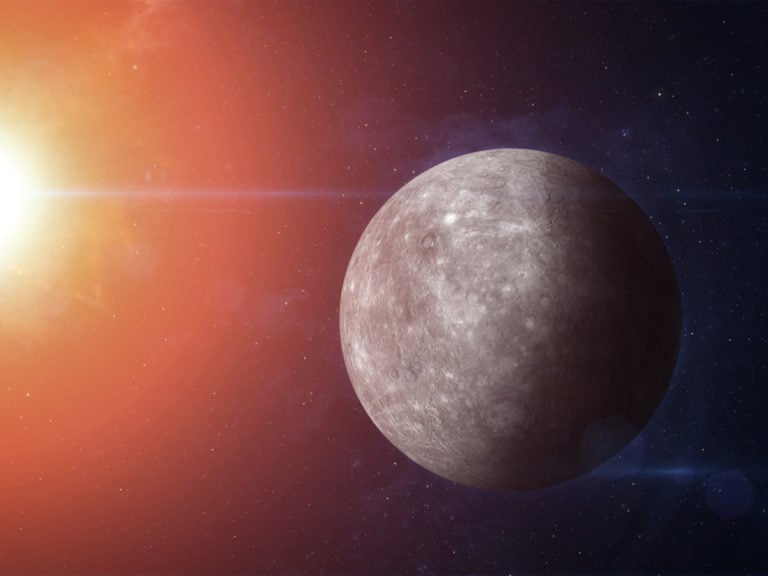

Mercury is the smallest and closest planet to the Sun in the solar system. It is quite difficult to observe Mercury from Earth due to its location. However, it is visible to the naked eye just after sunset or just before sunrise. The first described observations of the smallest planet in the solar system date back to ancient times.
Mariner 10 is the first spacecraft to approach Mercury. The shortest distance from Marinera to Mercury is only 327 kilometers. During the mission, about 2,500 images of the planet’s surface were taken. Mariner 10 became the first artificial satellite of the first planet in the solar system. His fuel supply has run out, but he is most likely still in orbit around the planet.
Venus
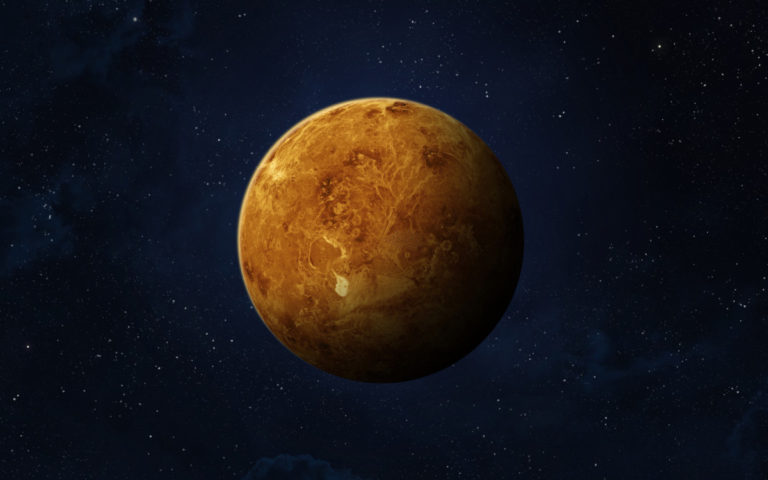

The second planet in the solar system, Venus is the brightest object seen in Earth’s sky after the Sun and Moon. Like Mercury, it is only visible just before sunrise or just after sunset, but its brightness makes it easy to observe.
Because of its size, chemical composition, and mass, it is often referred to as Earth’s sister (or twin planet). Unfortunately, conditions on its surface are not conducive to colonization. Atmospheric pressure is more than ninety times higher than the earth’s. The atmosphere is almost entirely composed of carbon dioxide and sulfur. The surface temperature is high, over 400 degrees Celsius. Most of the surface of Venus is formed by volcanic processes.
Earth
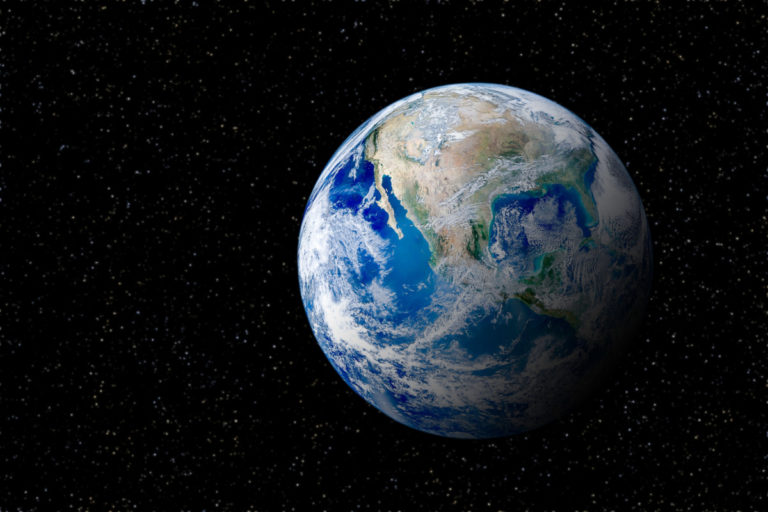

Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the fifth largest in the solar system. It is also the largest rocky planet. Earth is the only place in the universe where life exists. Our planet formed about 4.5 billion years ago.
Later, the first living organisms appeared on Earth, which now form the biosphere. The Earth’s atmosphere is a gaseous shell, consisting mainly of nitrogen and oxygen. The Earth’s atmosphere protects us from ultraviolet radiation and provides optimal conditions for various forms of life to thrive. The hydrosphere consists of all surface and ground waters. The lithosphere is the outer rigid shell of the Earth.
Mars

Mars has been explored by humans since 1965, when the Mariner 4 spacecraft made its first flyby of the planet. Six years later, the American Mariner-9 entered orbit, and a little later, the Soviet Mars-3 landed on the surface of the Red Planet.
Many Soviet and American unmanned probes landed on Mars, conducting a series of studies of the atmosphere and lithosphere and, of course, looking for any forms of life there. At present, even astronomical observations are being made from the surface of Mars.
Not so long ago (April 19, 2021), we witnessed the first controlled flight in the atmosphere of Mars of the Ingenuity drone, stationed there by the Perseverance rover. Each unmanned mission to Mars brings us closer to the first manned landing, which is scheduled for the 30s of the 21st century.
Jupiter
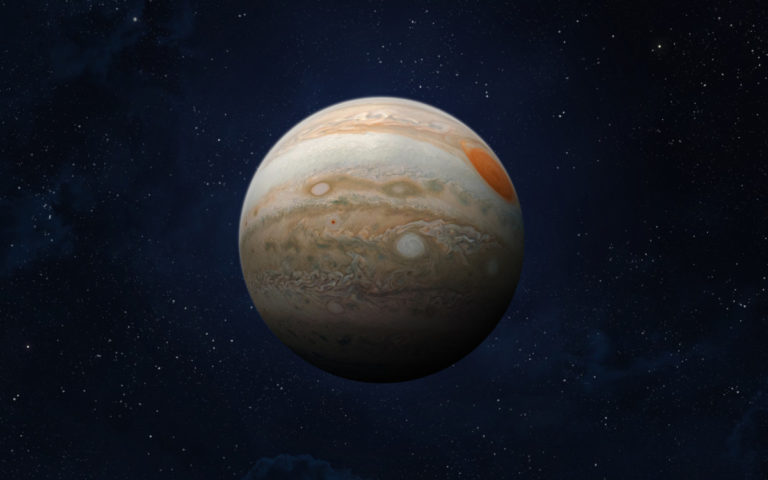

Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the first of the so-called gas giants. Jupiter is the largest planet in the solar system – its mass is estimated to be more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the solar system combined.
Because of its size, Jupiter is the fourth brightest celestial body visible in Earth’s sky after the Sun, Moon, and Venus. Jupiter is three-quarters hydrogen and one-quarter helium. This gas giant most likely has a solid stone core. At least 79 natural satellites revolve around it, the largest of which – Ganymede – is larger than Mercury.
To date, several exploration missions have been successfully sent to study this heaviest planet in the solar system. The Pioneer and Voyager programs were developed for the first photographs of the planet’s atmosphere.
Saturn

Saturn also has natural satellites. The planet has at least eighty-two moons. It is assumed that Saturn is similar in structure to Jupiter – it consists mainly of hydrogen and helium, as well as a solid core.
The first probe – Pioneer 11 – approached the surface of the planet back in 1979. The other, Cassini, orbited Saturn in 2004. During this mission, the occurrence of thunderstorms on the surface of Saturn, as well as the presence of hydrocarbon lakes and objects of extensive terrain, including lakes and mountains, were observed.
Uranus
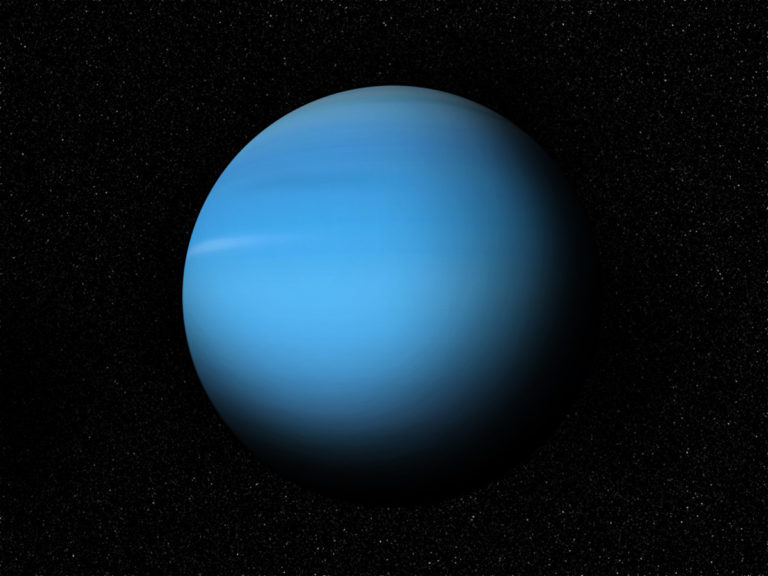
Consequently, Uranus is sometimes assigned to another group of planets called ice giants. An interesting fact is that the planet’s axis of rotation is close to the plane of its orbit, which means that the poles of Uranus are located where the equator of other planets is usually located. It was discovered only at the end of the 18th century and was initially mistaken for a star or a comet. The external structure of the planet is homogeneous – no weather activity is observed on its surface.
So far, only the unmanned aerial vehicle Voyager 2 has approached the atmosphere of Uranus. No new missions in this direction are planned.
Neptune
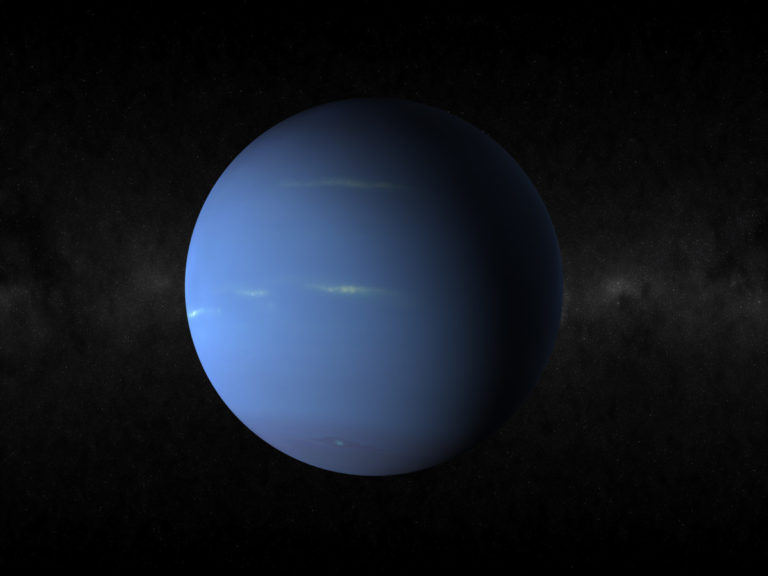
The eighth planet of the solar system is Neptune. Neptune is known as the twin brother of Uranus due to its size and the presence of ice in the atmosphere. Unlike its galactic neighbor, Neptune has distinct weather patterns shaped by the strongest winds seen in our planetary system.
The ninth planet? Pluto and other dwarf planets
The definition of the so-called dwarf planets is a relatively new phenomenon in astronomy – it was presented only in 2006. A dwarf planet is defined as a celestial body similar in shape to a spherical one orbiting the Sun that is not a satellite of another celestial body but has a much lower mass than a traditional planet.
Pluto was discovered in 1930. Until 2006, it was considered the ninth planet in the solar system, until the term dwarf planets was introduced. To date, five objects in our planetary system have been identified as dwarf planets – Ceres, Pluto, Haumea, Makemake, and Eris.
Not only planets – what else is there in the solar system?
The solar system is not only a group of eight planets and five dwarf planets. The structure of the solar system is much more complex. In orbit behind the four rocky planets (between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter) is the main asteroid belt with celestial bodies such as Ceres, Vesta, Pallas and Hygiea.
The asteroid system is so rare that many space probes have passed through it without encountering a single object in their path. In turn, beyond the orbit of Neptune is the Kuiper belt – a system of celestial bodies similar to the main asteroid belt, but definitely more massive and larger.
At least three dwarf planets orbit here: Pluto, Haumea, and Makemake. By 2020, two thousand bodies have been found in it, but it is assumed that there are at least seventy thousand objects with fairly stable orbits in the belt.
Beyond the orbit of Neptune, not far from the Kuiper belt, is the so-called scattered disk with many celestial bodies in orbits, the regularity of which is broken by the gravity of the gas giants. Some publications link the Kuiper belt to the scattered disk, and it is not entirely clear how to classify this distant part of the solar system.
The space filled with the solar wind is not a perfect sphere – the shape of the interaction is deformed by the gravity of individual planets, mostly gas giants. The scattered disk ends in the so-called heliopause – an imaginary layer in which the solar wind is balanced by the force of interstellar matter.
The outer part of the solar system is the so-called Oort Cloud, which is left over from the formation of our planetary system. This is a hypothetical cloud of cosmic particles that has never been explored before. Its distance from the Sun is a thousand times greater than the distance from the Kuiper belt to our central star.
The Oort Cloud is probably the place where many long-period comets are “born” that have been knocked out of their original orbit. Meanwhile, short-period comets most often originate from the Kuiper belt or scattered disk.