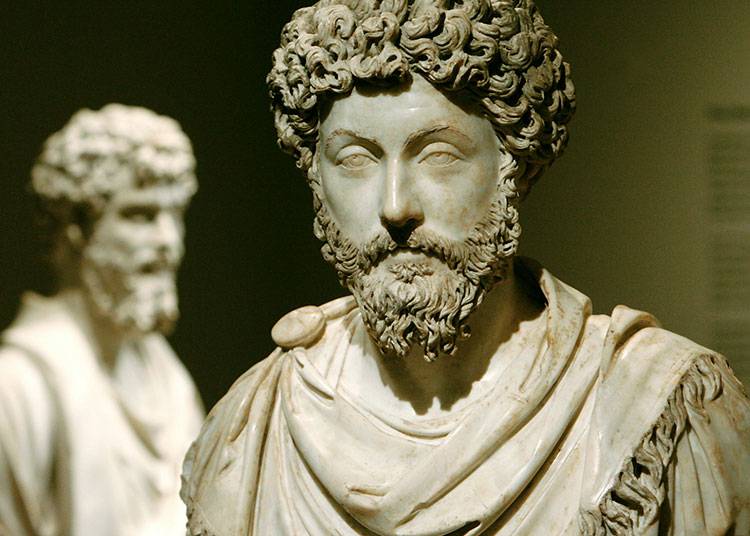
The founder of Stoicism, which arose around the year 300 BC. was Zeno of Citia, who acted as a teacher, and in the history of Stoicism, three main periods are distinguished, namely the older, middle and new standing.
Initially, Stoicism was known as “Zenonism”, after the name of its founder, and before the discovery of this philosophical school, the Stoics in Greece were called the community of poets who gathered in the Stoa Poikile. The founder of the school could not afford a building like the Lyceum of Aristotle or the Academy of Plato, and therefore taught his followers in the marketplace, where anyone could join the debate.
Representatives of Stoicism
The ancient standing existed in the III-II centuries BC, and Stoicism gained popularity among the educated elite of Greece and Rome. In addition to Zeno of Kitia, Cleanthes, Zeno of Tarsus, Diogenes of Babylon, Ariston, Crates of Mallus, and many others can be distinguished here.
The middle one, which is usually called Stoic Platonism, existed in the II-I centuries BC. The main representatives are Hekaton of Rhodes, Diodotus, Athenodorus, Panetius of Rosdos.
Late standing falls on the I-II centuries AD. Here the most striking figures are Seneca, Epictetus, and also Marcus Aurelius. As a result, Stoicism moved closer to Neoplatonism, and eventually dissolved into the latter.
The essence of stoicism and the main ideas
Diogenes Laertes divided the teachings of the Stoics into three parts, namely physics, ethics and logic, and such a division, according to E. Zeller, was borrowed from the Platonists.
In addition, two more comparisons with an animal and an egg are known, where in the first case, the indicated logic, physics and ethics represent bones, meat and soul, while in the second case they are shell, protein and yolk.

In the concept of the Stoics, truth is formed directly in the process of a thorough process of understanding the perceived reality, and Sextus Empiricus noted that the Stoics recognized only a certain part of the sensed and conceivable as true. Truth, according to the Stoics, is a kind of product of the consent of the intellect with the essence of the object, which is of an objective nature, and such consent requires certain efforts, which only the sages are capable of. The corresponding division into “wise men” and “fools” caused the abolition of the concept of reason as a god, which is the determinant of everything that exists, except for itself.
The mind of the Stoics was preserved as the root cause of everything, but this is in relation to physics, while in logic the mind acquired the ability to determine the truth directly in terms of assessing the most diverse phenomena of reality. The attitude of the Stoics to the state, who considered public imperial relations far from justice, was predetermined by their direct philosophical doctrine, which caused the emergence of the concept of “cosmopolis”.
Logic
It consists of rhetoric and dialectic, which means the science of speaking and the science of arguing, respectively. The starting point of the Stoic theory of knowledge is matter, and Zeno argued that perception, which changes the state of the material soul, leaves an imprint in it, as in wax.
Physics
According to the Stoics, the surrounding world is a kind of living organism, which is controlled by the logos, while the fate of a person is its projection. According to Stoicism, everything that exists, which has a bodily character, differs only in the degree of “roughness” of matter.

The Stoics noted that reality is perceived exclusively in a subjective sense, while “objective” perception is impossible by nature. The Stoics considered theoretical thinking to be the only way to realize the knowledge of truth, and empiricism not only did not act as the main criterion for the correctness of reasoning, but was generally ignored in this regard, yielding its position to “theoretical truth”.
Ethics
The main idea of the ethics of Stoicism is the teleologically predetermined course of history, and the main goal of man, according to the Stoics, is to be in harmony with nature.
The Stoics distinguish four main types of affects that should be avoided, namely: pleasure, lust, disgust and fear, while they adhered to skepticism about the possibility of changing society, based mainly on knowledge, in connection with which they considered it rational to preach wisdom that is of an individual character, separating her from society as a whole.
Roman Stoicism
During the Roman Empire, the philosophy of Stoicism turns into a kind of religion for the people, gaining the greatest influence on the territory of Syria and Palestine. Socrates remained the main authority for the Stoics, and above all the sage’s assertion that injustice in the end causes much more harm directly to the one who commits it, and not at all to the victim.
As for Plato, the Stoics did not accept his doctrine of ideas, rejecting the numerous arguments of the philosopher about immortality. Although the later Stoics agreed with Plato that the soul is immaterial, early Stoicists adhered to Heraclitus’ point of view, according to which the soul is based on material fire.