The development of mankind is determined by geniuses who have managed to discover something new. Each step in the history of human society is somehow connected with the development of science, with significant personalities who made breakthroughs in a particular field of knowledge. One of these people was Albert Einstein, whose extraordinary views on the structure of the world to a certain extent shaped modern society and carried out a radical revolution in science.
Early years
Albert Einstein was born in 1879 in Ulm, Germany, to a poor Jewish family. Even at school, he showed a penchant for mathematics and physics; to a certain extent, his scientific growth was helped by life circumstances – his father began to trade in electrical equipment, prominent scientists of that time taught in educational institutions in Germany and Switzerland, where Einstein was educated.
In addition, in 1902, Albert Einstein received a position as a Class III Examiner at the Federal Invention Patent Office in Bern, Switzerland. In 1933, due to the growth of fascism in Europe, the scientist was forced to move to the United States, where he died in 1955.
Scientific discoveries
Einstein’s discoveries turned out to be so revolutionary for their time that, having been repeatedly nominated for the Nobel Prize in physics, he received an award for … studying the photoelectric effect: this area of physics turned out to be the most demanded and understandable to the scientific world of that time. The secretary of the Swedish Academy of Sciences directly informed the scientist that the rest of the work (on the theory of gravity and the theory of relativity “will be evaluated after their confirmation in the future”).
Modern science is impossible without the achievements of Albert Einstein. He, like Newton in his time, changed the generally accepted views on the structure of the world, turned the hard and dry world of Newton’s gravitational interactions into a flexible one, taking into account the curvature of space and time. This leap is beginning to be fully appreciated only now, at the beginning of the era of space exploration: developments “grown up” from the theory of relativity make it possible to control interplanetary spacecraft, explore other solar systems and galaxies.
The theory of relativity and the theory of gravity have become fundamental concepts on which many branches of modern science are based – astronomy, physics, cosmology. In addition to independent work, Einstein actively collaborated with the most prominent scientists of his time – Marcel Grossman, Robert Brown, Shatyendranath Bose. One of the fruits of this collaboration is the discovery of the fifth aggregate state of matter, the so-called Bose-Einstein condensate: in this state, the temperature of matter is close to absolute zero, and quantum effects begin to manifest themselves at the macroscopic level.
For example, the fastest type of communication is fiber optic: the data transfer rate can reach several terabits per second. Motion and light sensors are widely used to automate the operation of lighting systems, conveyors, even doors in garages and supermarkets.
Last years of life
Einstein’s achievements have firmly entered modern life. Unfortunately, people rarely remember the humanism and philanthropy of the scientist – who at the beginning of his life knew poverty and deprivation, faced with fascism, until the end of his life, Albert Einstein often used his influence to protect humanitarian values. For example, he several times asked Stalin to mitigate the fate of the repressed foreign scientists, addressed the US leadership with a warning about the development of nuclear technology, and, in particular, the creation of new types of weapons.
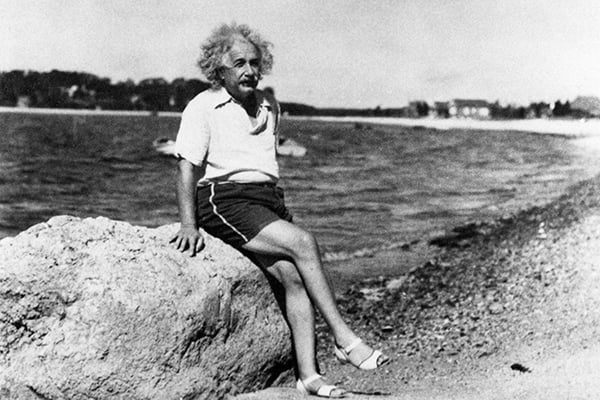

Einstein considered participation in the American nuclear program the greatest tragedy of his life, since he saw what his work ultimately led to. There is a legend that shortly before his death, the scientist burned his developments regarding the so-called “Philadelphia experiment”, during which he tested his theory of the “unified field”. If so, then perhaps this person saved all of humanity from the emergence of a new class of weapons of mass destruction – unfortunately, any scientific developments are evaluated primarily by the military.
At the same time, Albert Einstein was not a religious person in the truest sense of the word – he did not believe in a “personified God” – an independent being that controls the destinies of people and evaluates their actions.
Shortly before his death, the scientist wrote: “If there is anything in me that can be called religious, it is only boundless admiration for the structure of the world, as far as our science can comprehend it.”